Dear Readers,
Hope you had a good time learning about the effects of Yoga on functional and metabolic changes in brain (2/n) (Give it a read if you haven’t). Now let’s delve further and learn more about the effects of Yoga on Endocrine System.
You will appreciate the effects of Yoga only when you know how amazing our endocrine system is, it basically regulates every aspect of our bodily functions. To bring every reader on the same page, this post is dedicated to make you aware of the functions of our Endocrine Glands and what happens when they get dysfunctional (3.1/n).
How Yoga helps balance this system will be discussed in the next article (3.2/n) which will follow in a few days.
The TL;DR*
The endocrine system is made up of several ductless organs called glands that make hormones. Hormones are the body's chemical messengers.
Endocrine glands are all over your body: brain, neck, lungs, kidneys, stomach, pelvic region. We have around 10 important endocrine glands. Pituitary gland is endocrine system’s master gland.
The smallest endocrine gland (parathyroid) is about the size of a rice grain and the largest (pancreas) is 6 inches long.
Our endocrine glands control almost every aspect of our body: sleep, reproduction, body temp, blood pressure, calcium levels, metabolism, mood, hunger, movement, growth, respiration, sensory perception, etc.
Commonly known diseases caused by endocrine gland dysfunctions are: diabetes mellitus, Poly Cystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), Obesity, Addison’s disease, Hypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism, Cushing’s syndrome, Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, Prolactinoma, Acromegaly, etc.
Endocrine diseases can be due to three main causes: 1) Underproduction of a certain hormone; 2) Overproduction of a certain hormone; 3) A malfunction in the production line of a hormone or in its ability to function correctly.
If you skew the endocrine system, you lose the pathways to self. When endocrine patterns change, it alters the way you think and feel — Hilary Mantel
For those who love the details….
Before understanding the effects of Yoga on endocrine system, let’s first get to know this fascinating system which helps to run our body properly: Endocrine System
The word endocrine (pronounced: EN-duh-krin) derives from the Greek words "endo," meaning within, and "crinis," meaning to secrete. The endocrine system is made up of several ductless organs called glands that make hormones. Hormones are the body's chemical messengers. Chemically, hormones may be classified as either steroids (sex hormones and those from the adrenal cortex) or protein (rest of the hormones). They carry information and instructions from one set of cells to another to control many different bodily functions, including:
Respiration
Metabolism (the way you break down food and get energy from nutrients).
Reproduction
Sensory perception
Movement
Sexual development
Growth
Sleep
Hormones are very potent substances, their functions are tightly controlled by negative feedback mechanism in order to maintain a state of stability or homeostasis.
Watch the Ted Ed video if you are interested to learn more about how hormones work (some really cool biology!!):
Endocrine glands are all over your body,
Brain: hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and pineal gland
Neck: thyroid and parathyroid glands. The parathyroid glands are about the size of a grain of rice (smallest gland)
Lungs: thymus is located directly behind your sternum and between your lungs
Kidneys: adrenals are on top of your kidneys
Stomach: the pancreas is behind your stomach. Pancreas is the largest gland, about 6 inches long. Interesting fact: pancreas has both endocrine and exocrine functions.
Pelvic Region: Ovaries (if you're a woman) or testes (if you're a man)
Want to know some more surprising facts about endocrine system, click here.
Now, let’s get familiar with the crucial functions of our endocrine glands:
Hypothalamus is the boss of pituitary gland. It gives instruction to pituitary gland to either start or stop making hormones.
The Pituitary gland is endocrine system’s master gland. This gland controls many functions of the other endocrine glands. Some important hormones produced by this gland are:
Growth hormone — stimulates the growth of bones, muscles, and other organs
Thyroid-stimulating hormone, or thyrotropin — causes the glandular cells of the thyroid to secrete thyroid hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone — stimulates the secretion of cortical hormones
Gonadotropic hormones — regulate the development, growth, and function of gonads, testis and ovaries
Prolactin hormone — stimulates milk production after the birth of the infant.
Antidiuretic hormone — promotes the reabsorption of water by the kidney tubules
Oxytocin — causes contraction of uterus and also stimulates the ejection of milk from the lactating breast
Just to release pressure of heavy sciency words!!
Pineal body produces the hormone melatonin, which regulates the daily physiologic cycles and also affects reproductive development.
The thyroid gland plays an important role in maintaining the body’s homeostasis by producing hormones that regulate the body's metabolism. It produces two vital metabolic hormones:
Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)
Calcitonin — which works as an antagonist (opposite) to the Parathyroid hormone.
The parathyroid glands plays crucial role in calcium homeostasis. Calcium helps to maintain healthy bones and teeth, it also helps in stimulation of neurons and muscle cells by secreting:
Parathormone— play an important role in the regulating body's calcium balance. Parathyroid and Calcitonin hormones work together to maintain the vital homeostatic balance of calcium ions in the blood.
Thymus: It produces white blood cells that fight infections and destroy abnormal cells.
Adrenal gland: Like many glands, the adrenal glands work hand-in-hand with the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Chemically, all the adrenal hormones are steroid. The adrenal glands make and release
Aldosterone — which acts to conserve sodium ions and water in the body.
Cortisol — which increases blood glucose levels.
Androgens (male hormones) and Estrogens (female hormones)
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine — these are secreted in response to stimulation by sympathetic nerve, particularly during stressful situations that maintain blood pressure and regulate metabolism.
Pancreas: The pancreas plays a role in digestion, as well as hormone production. Hormones produced by the pancreas helps to regulate levels of blood sugar
Insulin and
Glucagon, which regulate levels of blood sugar.
Ovary: In addition to containing the egg cells necessary for reproduction, the ovaries also produce estrogen and progesterone.
Testis: The testes produce testosterone and sperm.
In addition to these major endocrine glands, some other organs also have minor hormonal activity as part of their function. These include:
Stomach: produces gastrin which stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid and the enzyme pepsin to aid the digestion.
Small intestines: secretin and cholecystokinin which helps in neutralizing stomach acid and releasing bile, respectively.
Heart: produces atrial natriiuretic hormone, or atriopeptin.
Placenta: is a temporary endocrine gland. It produces human chorionic gonadotropin, which signals the mother's ovaries to secrete hormones to maintain the uterine lining.
Adapted from Functions of Endocrine Glands by Fred, 2018
Causes of endocrine disorders
Endocrine diseases can be due to three main causes:
Underproduction of a certain hormone
Overproduction of a certain hormone
A malfunction in the production line of a hormone or in its ability to function correctly.
Types and causes of endocrine disorders are tabulated in the chart below:
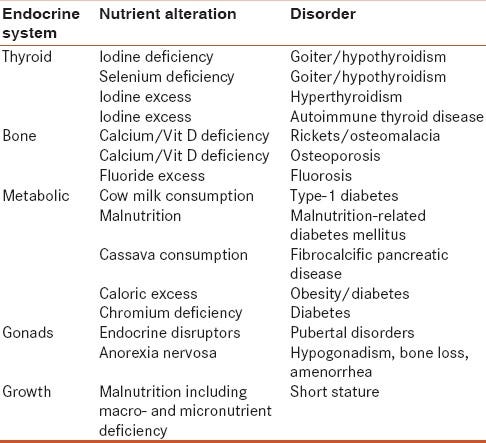
I hope you enjoyed reading this article and after knowing about Endocrine System multiple functions, you must be curious to know how Yoga can help to keep our endocrine system in sync ! In the next article (3.2/n), I will cover the science behind the effects of Yoga on the Endocrine System.
If you found the article of interest or have thoughts about what you’ve read here, please do share in the comments section below. It will help guide my future posts.







Very interesting article. Good explaination.