Can Light Impact our Biology - Part 3 ?
Everyday, Everywhere stories through the lens of science
Dear Readers,
Now you can hear this article!
This is the final article of 3-part series exploring the question we asked two weeks back - Can light impact our Biology ?
For simplicity, we focussed first on the visible spectrum of light (part-1), then we unraveled the impact of short wavelength spectrum (gamma rays, X-rays and UV rays) on our biology (part-2). In this article, we will understand all about long wavelength spectrum which includes infra-red radiation, microwaves and radio waves.
The long wavelength spectrum is referred to as non-ionising radiations. If you recall from the earlier post, ionising radiations can penetrate matter and damage it by breaking the chemical bond and releasing atomic energy. Henceforth, in optimised doses ionising radiations like gamma and X-rays find applications in cancer therapy. In contrast, energy of long wavelength spectrum is less and are thus non-ionising in nature. Energy of radiation is inversely proportional to its wavelength. That is, when the wavelength increases, energy decreases and when the wavelength decreases, energy increases. In this regard, microwaves and radio waves cannot pose deleterious effect on our Biology. But, because of their unique characteristics they find use in many applications like industrial, scientific, military, commercial, and medical
Let’s explore them one by one, we will understand both the harmful and useful effects of this spectrum!
By the end of this article you will appreciate how light is tightly integrated in our lives and can affect our biology in so many ways.
Let’s start with:
1. Infra-Red (IR) radiation
We cannot see IR rays but we can feel them as heat. Thus, they are also referred to as heat rays. They were discovered by William Herschel, a British astronomer in 1800, when he was attempting to measure the difference in temperature between the colours of the visible spectrum by a thermometer. He observed an increase in temperature from blue to red, and he found an even warmer temperature measurement just beyond the red end of the visible spectrum, this invisible but heat emitting radiations were called as infra-red (beyond the red) radiations.
Harmful effects of IR radiations
Effect of IR radiations on Climate change
IR rays are naturally produced from Sun and Fire. The Sun gives off half of its total energy as IR. Even the visible light which comes from Sun and absorbed by Earth is emitted back in the form of IR rays. The balance between absorbed and emitted infrared radiation has an important effect on Earth's climate.

Let’s understand this — Today, about 71% of the sunlight that reaches the Earth is absorbed by its surface and atmosphere. Absorption of sunlight results in increase in temperature of the land, air, or water. This energy is then re-radiated by the Earth as heat radiation. The more sunlight a surface absorbs, the warmer it gets, and the more energy it re-radiates as heat. This heat is then absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases and clouds, initiating a vicious cycle which traps the heat radiation into Earth’s atmosphere, resulting in global warming. This phenomena is called greenhouse effect. Carbon dioxide, methane and water vapour are majorly responsible for global warming. Largely due to human activity, the levels of heat trapping greenhouse gases are increasing and so is the land and water temperature.
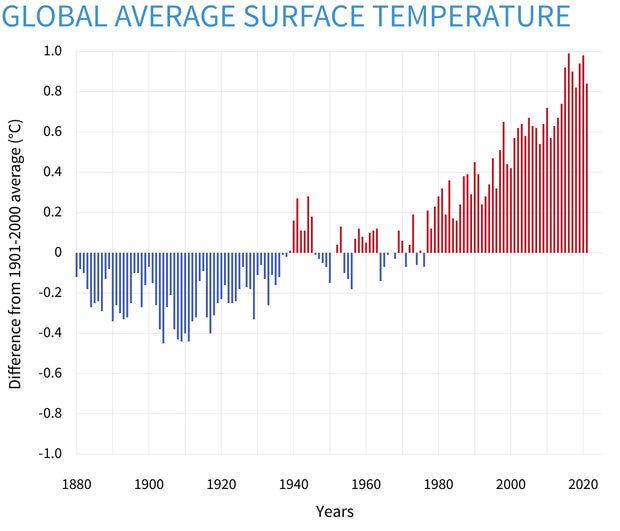
Do you know? Averaged across land and ocean, the 2021 surface temperature was 0.84°Celsius warmer than the twentieth-century average and 1.04˚C warmer than the pre-industrial period (1880-1900). This is actually huge! The foot-prints of global warming can be seen everywhere. Leave me a comment, if you want to learn more about Global warming and its impact ?
Effect of IR on eye and skin
If exposed directly on eyes, IR rays can be hazardous to the eyes, resulting in damage or even blindness to the user.
It can also induce premature aging of skin, if you are exposed to strong IR radiations for long periods of time. However, at low levels, IR radiations are being used therapeutically to stimulate, restore and heal skin. More on this can be found under the benefits section.
Benefits of IR radiations
IR radiations emitted by our bodies
Our bodies can also absorb heat from surroundings and emit thermal (IR) radiations. The amount of thermal radiation emitted by an object depends on its surface temperature, area and characteristics. Warmer object emits more thermal radiation than cooler one. This is applied to measure body temperatures by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by human bodies using handheld infrared ear or forehead thermometers. We see their use at airports, ports and border crossings, where infrared cameras are widely used for fast screening of travelers with a fever. However, thermal images of a person captured using an infrared camera just indicate the temperature of the person's skin, and cannot be used to diagnose diseases happening below the skin.
IR as therapy for Skin related conditions
This is a fast evolving technology to treat multitude of skin related conditions. Skin is the one organ in our body which is exposed to light at all times, still it responds to red light or near infra-red light. High-efficiency semiconductors (LEDs) are utilised to produce light in the near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. The photons of light are absorbed by chromophores (light absorbing pigment) in skin cells, such as mitochondrial cytochrome C, endogenous protoporphyrins, and melanin which consequently results in activation of diverse signalling pathways, increase the blood flow and also can activate stem cells. Together these pathways helps to increase tissue repair and healing.
In dermatology, this therapy called Low-level Laser Light Therapy (LLLT) has beneficial effects on wrinkles, acne scars, hypertrophic scars, and healing of burns. It can also help to reduce UV damage both as a treatment and as a prophylactic measure. In pigmentary disorders such as vitiligo, LLLT can increase pigmentation by stimulating melanocyte proliferation and reduce depigmentation by inhibiting autoimmunity. Inflammatory diseases such as psoriasis and acne can also be managed. Light (LED) treatments are safe and well tolerated by patients. However, some people can have mild adverse events like pigment changes, dryness, redness of the skin, skin peeling, and stinging.
To correct colour vision in aged population
Recent study reported that a single 3 min exposure to 670 nm light (long wavelength light), at much lower energies, was sufficient to significantly improve colour vision in ageing populations. They observed that brief exposure of long wavelength light to the eyes was able to increase the efficiency of retinal cone cells of aged individuals for up to 1 week. Though clinical studies are needed to validate this single study, but this is an economical and simple technique to increase the colour vision in elderly people.
Night Vision possible with IR radiations
Our eyes cannot see properly in dark but there is a whole world which is active in dark and we are curious to explore. IR radiations comes handy, with IR equipped night vision equipment like night vision goggles and scopes we can now see up to 1,000 yards away on a dark night. These night vision equipments sense and capture small amounts of IR light that are reflected off objects and then electrically amplifying that light into a characteristic glowing green image, this technique is called optoelectronic image enhancement. Now with an advanced technology, we can do digital image enhancement, where full colour image can be created instead of the old-school glowing green images. Watch the below National Geographic video to get an idea of how night vision is opening up the whole new world to us!
Do you know ? Snakes possess a unique sensory system for detecting infrared radiation, enabling them to generate a 'thermal image' of predators or prey. But not all snakes have the ability to produce a thermal image in the dark.
Use of IR radiations in household
IR rays find their use in wide variety of household, appliances such as toasters, incandescent bulbs and heat lamps, which use these rays to transmit heat. If you have used incandescent bulb, you will know that these bulbs get super hot once in use. It is because, only 10% of their energy input is converted into visible light, while the other 90% is converted to IR or heat radiation.
TV remote controls also rely on IR radiations, they shoot out pulses of IR energy from a LED to an IR receiver in the TV. The receiver then converts the light pulses to electrical signals that instruct a microprocessor in the TV to carry out the programmed command. In this way, IR lasers can be used for point-to-point communications over distances of a few hundred meters or yards.
IR Saunas
IR lamps are also widely used in saunas. In IR saunas heat is directly absorbed by the body, instead of heating the air first and indirectly heating body as in traditional saunas. With IR saunas, penetration of heat is deep and benefits can be achieved with lower temperature, 60 deg celcius as compared to 80-90deg celcius in traditional saunas.
IR rays also find their use in tracking, communications, meteorology, astronomy, cleaning, analysis and conservation of art.
In gist, IR or heat radiations are tightly interwoven with our biology. We use them to in our household, industries, medical, military, imaging and weather forecasts.
2. Microwaves
Microwaves are the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum which lies between IR rays and radio waves, with wavelengths between 1 mm and 1 m. Even at the highest frequency, the energy per photon is too low to produce ionization, which means that microwave photons do not contain sufficient energy to ionize molecules or break chemical bonds, or cause DNA damage. The word "radiation" refers to energy radiating from a source and not to radioactivity.
In 1965, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, scientists at Bell Labs, made an incredible discovery: they serendipitously discovered the cosmic microwave background radiation. This radiation, which fills the entire universe, is a clue to its beginning, known as the Big Bang.

Microwaves can be propagated as continuous or pulsed wave. The continuous wave energy is used mostly in communication and in fundamental research work. The pulsed wave is widely used in radar systems, industrial equipment, and medical diathermy devices.
Harmful effects of Microwaves
Microwaves can cause localised heating in the body. The microwave energy is absorbed and gets converted to heat, this happens because the electromagnetic fields cause polar molecules such as water and fat to rapidly vibrate within the field and results in localised heating. Exposure to high levels of microwaves can cause a painful burn. In areas or organs in which there is a relatively poor blood supply, the temperature may rise more rapidly and to a higher degree than in the rest of the body. Classical examples of such organs are the eye and the testes, and these are actually the most susceptible organs to microwave damage. The lens of the eye is particularly sensitive to intense heat, and exposure to high levels of microwaves can cause cataracts, as in accidental overexposure of radar workers. But these types of injuries – burns and cataracts – can only be caused by exposure to large amounts of microwave radiation.
Microwaves from cell phone transmissions
Our skin can absorb frequencies above 10 GHz, cell phone transmissions while frequencies lower than 1 GHz–TV or radio transmissions say–are thought to be reflected without much energy transfer. There are evidences that cell phone signals have supposedly influenced human health and behaviour. The list of symptoms includes depression, sleep loss, changes in brain metabolism, headaches and so on. However, there is a substantial body of epidemiological evidence that finds no connection between adverse health effects and cell phone exposure. What’s more, physicists point out that the radiation emitted by cell phones cannot damage biological tissue because microwave photons do not have enough energy to break chemical bonds. More studies are needed to understand the relation between phone emitted microwaves on our health but till then it is advisable to avoid overuse of phone, use earphones if your job needs more talking on phone, keep phones away from bed, don’t keep phone in your pockets for long, etc.
Useful effects of Microwaves
Microwave thermotherapy
Microwave thermotherapy is generally used to treat hyperplastic prostate tissue. It involves the insertion of a specially designed urinary catheter into the bladder, allowing a microwave antenna to be positioned within the prostate; there, it heats and destroys hyperplastic prostate tissue.
Treatment of warts
Microwaves are also used to treat warts associated with Human papilloma virus infection. Most therapies, including cryotherapy, laser, and radiofrequency devices show low efficacy and induce discomfort through tissue destruction. Microwaves are readily capable of passing through highly keratinised skin to deliver energy and induce heating of the tissue in a highly controllable, uniform manner.
Ablative treatments of Liver Tumor
Microwave therapy quickly treats tumors that are otherwise difficult to eradicate and it does so with minimal damage to healthy tissues. When tumors are deep inside liver, the body's largest organ and so rich with blood vessels that any surgery is tricky. With microwave ablation, a surgeon makes a small incision, guided by imaging, finds the tumors and applies microwave heat to them to destroy them. The body then absorbs the dead tissue.
Microwave ablation offers an option for a significant number of people who may feel like they've run out of options-Gloria Hwang, MD, interventional radiologist, Stanford Hospital & Clinics
Cooking/re-heating food
Microwaves are reflected by metal but they pass through glass, paper, plastic, and similar materials and they are absorbed by foods. When absorbed the microwave energy is converted into heat energy, which heats the food. These properties of microwaves make them ideal to be used in microwave ovens.
Have you ever experienced that sometimes food cooked in microwave has hot outside but inside is totally cold. Majority of time this happens when bigger portions, thicker food or cooking time is less than optimal. This phenomena happen because microwave ovens do not cook food from the inside out. Outer layer of food is heated and cooked primarily by microwave while the inside is cooked mainly by the conduction of heat from the hot outer layers. Microwave cooking does not reduce the nutritional value of foods any more than conventional cooking.
A Federal standard limits the amount of microwaves that can leak from an oven throughout its lifetime to 5 milliwatts of microwave radiation per square centimeter at approximately 2 inches from the oven surface. This limit is far below the level known to harm people. Microwave energy also decreases dramatically as you move away from the source of radiation.
Other uses
Microwaves are used to detect speeding cars and to send telephone and television communications. Industry uses microwaves to dry and cure plywood, to cure rubber and resins, to raise bread and doughnuts, and to cook potato chips.
There are many false allegations/fake news reporting the deleterious effects of microwaves on health, but, it has not been shown conclusively that microwaves have significant adverse biological effects at low levels.
3. Radio Waves
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. They range from the length of a football to larger than our planet. Heinrich Hertz proved the existence of radio waves in the late 1880s. Radio waves are emitted from Sun or from any astronomical object that have a changing magnetic field can produce radio waves. By studying the radio waves originating from these sources, astronomers can learn about their composition, structure, and motion.
Harmful Effects of Radio waves
Radio waves are non-ionising radiations like microwaves and thus does not pose any serious damage to DNA and hence cannot cause cancer. However, If radio waves is absorbed by the body in large enough amounts, it can produce heat. This can lead to burns and body tissue damage, especially eyes and testis are more susceptible.
Some people can have significant radio waves exposure as part of their jobs. This includes people who maintain antenna towers that broadcast communication signals and people who use or maintain radar equipment. Most people are exposed to much lower levels of man-made radio waves every day, ones emitted from radio and television broadcasts, WiFi and Bluetooth devices, cell phones (and cell phone towers), and other sources. Radio waves can cause physiological and/or morphological effects on bees, plants and trees.
Whether cellphones, cell phone towers and other devices which emits radio waves can have serious risk to human health is area of active research and lot of conflicting studies. We will discuss this issue in detail another time as it is beyond the scope of this post.
Useful effects of Radio waves
Communication
Radio waves are widely used for communication. You can tune a radio to a specific wavelength—or frequency—and listen to your favorite music. The radio "receives" these electromagnetic radio waves and converts them to mechanical vibrations in the speaker to create the sound waves you can hear.

They are used in Global positioning system (GPS), a system of satellites, ground stations, and receivers that receive high-frequency wave signals, amplify them, and return them to earth. We rely on GPS when we travel to get us to our destination.
Medical uses
Radio waves, like micro waves can penetrate skin and generate heat, this makes them useful in several medical procedures like radio waves diathermy, hyperthermy treatment of cancer, electrosurgery and radiofrequency ablation.
Diathermy is use of radio waves induced heat as a form of physical therapy, commonly used for muscle relaxation. Surgically, the extreme heat that can be produced by diathermy may be used to destroy neoplasms, warts, and infected tissues, and to cauterize blood vessels to prevent excessive bleeding. The technique is particularly valuable in neurosurgery and surgery of the eye.
Radio waves are also used in Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to generate images of the human body.
Conclusion
Light is everywhere, it affects our Biology even when we can't see it. It is overwhelming to realise how our physiology is in sync with the light and how unknowingly the things which improve our lives can do damage to this perfectly synced system. It is important for everyone to understand the impact of light on our Body, because then only you can be empowered with knowledge to optimise the health of your mind and body.



